

Below you'll see diagrams along with the names of the back muscles that may be the cause of your pain. Likewise, there are muscles in other parts of the body that help support and move the spine. For example, some muscles located in the chest also help move the shoulders. Other muscles beyond the back also help move the head, shoulders, arms, and legs. There are groups of muscles that move the: The back has different muscle groups that work together to allow movement. Moving deeper into the body, there are intermediate muscles and deep muscles. Some are closer to the surface (called superficial muscles).
#Spine muscles free
If you are experiencing back pain, take a free Goodpath assessment for a personalized back pain program designed just for you:Īs with other parts of the body, the back has several layers of muscles. What could cause a muscle and tendon strain? Bending and lifting a heavy package. So, activities that cause a strain could injure both the muscle and tendon at the same time. There are tendons at the ends of the muscles, which attach to the bone. What could cause a tendon strain? Overusing a tendon without allowing for rest. Like with muscles, tendon stretches and tears are also called strains. What could cause a muscle strain? Recovering from quick movements like a loss of balance. Strained muscles can occur anywhere in the back, but often affect the low back (lumbar area). These terms describe a stretched or torn muscle. Many people have experienced or heard of a strained muscle (also called a pulled muscle). Sometimes, muscles and tendons are strained at the same time. One type of injury – a strain – means that a muscle or tendon has stretched or torn. But, they are common in the back and can cause pain. Muscle or tendon injuries can occur anywhere in the body. They help support particular bones and make them move. In the back and elsewhere in the body, tendons attach muscles to bones. The fleshy, thick part of the muscle is called its belly. On the other hand, the insertion is where a tendon attaches that muscle to the *more* movable bone. By tightening and relaxing, the skeletal muscles create movement.Įvery skeletal muscle has three main parts: *the origin, insertion, and belly.* A muscle’s origin is where a tendon attaches it to the *less* movable bone. They support bones, in this case, the vertebrae. There are three different types of muscles in the body: the heart muscle, smooth muscles, and skeletal muscles. Certain back muscles extend to other areas, like the shoulders, upper arms, and thighs. Other muscles are small and cover much less space. Some of these muscles are quite large and cover broad areas. The back’s muscles start at the top of the back (named the cervical vertebrae) and go to the tailbone (also named the coccyx).
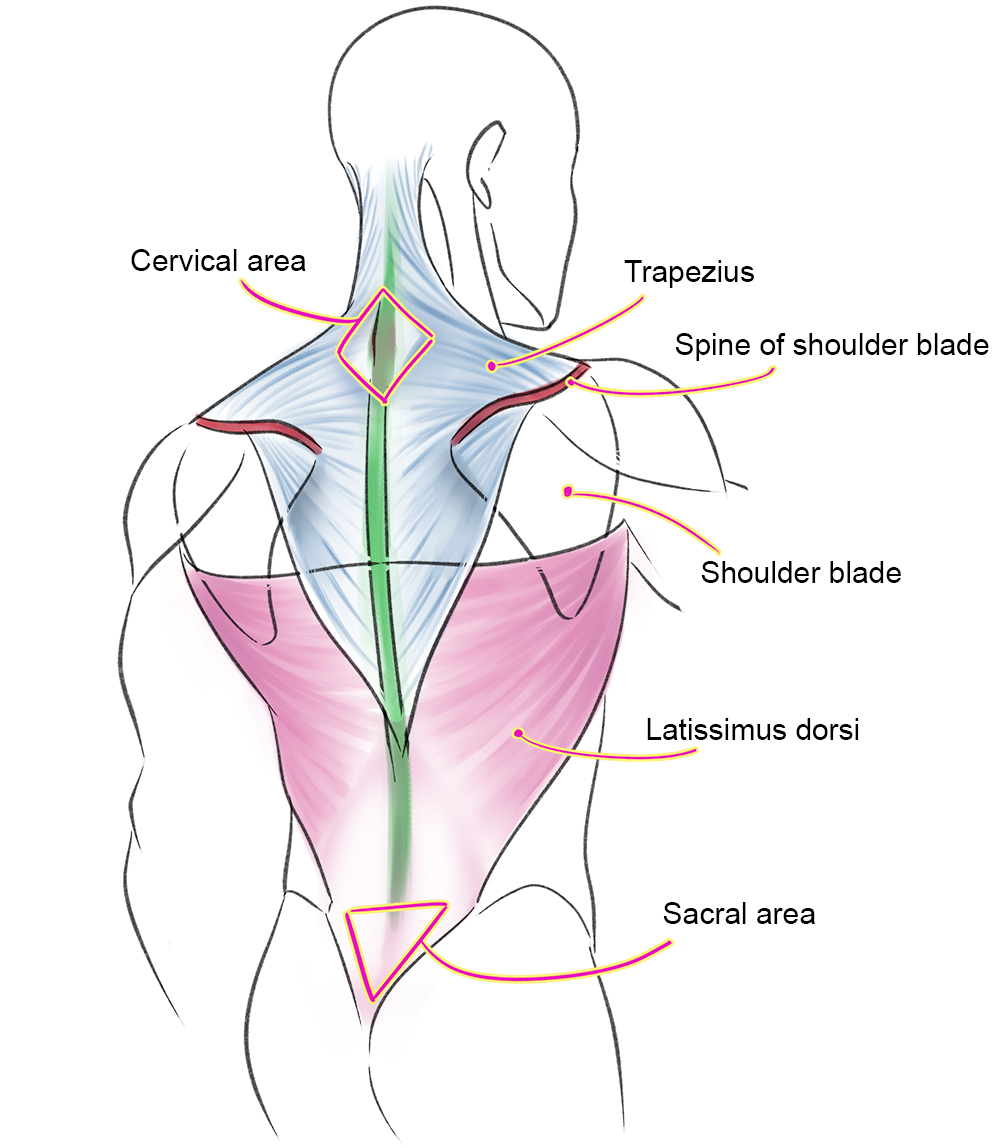
These muscles support the spine and allow for movement. Tendons attach the muscles to the vertebrae. Nerves extend through small holes in the vertebrae to different parts of the body. The spine is made up of bones called vertebrae.īetween each vertebrae, discs provide cushioning. Each of these parts are individual structures, which function or work together. It is made of the spine, discs, nerves, muscles, tendons, ligaments, and other structures. The Back’s Structure The back’s structure is complex.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
